Essential roles and responsibilities in a warehouse (updated 2024)
.png)
Warehouses are vital hubs in the supply chain, ensuring goods are efficiently stored, managed, and distributed. A well-run warehouse depends on the coordination of key roles, each contributing to smooth operations and productivity. Understanding these roles in detail is essential for effective management.
Read more: Discover how WMS systems enhance warehouse operations in our article "What is WMS?"
Organizational Structure
A streamlined warehouse structure fosters efficiency and accountability. Below is a basic organizational chart to illustrate the hierarchy:
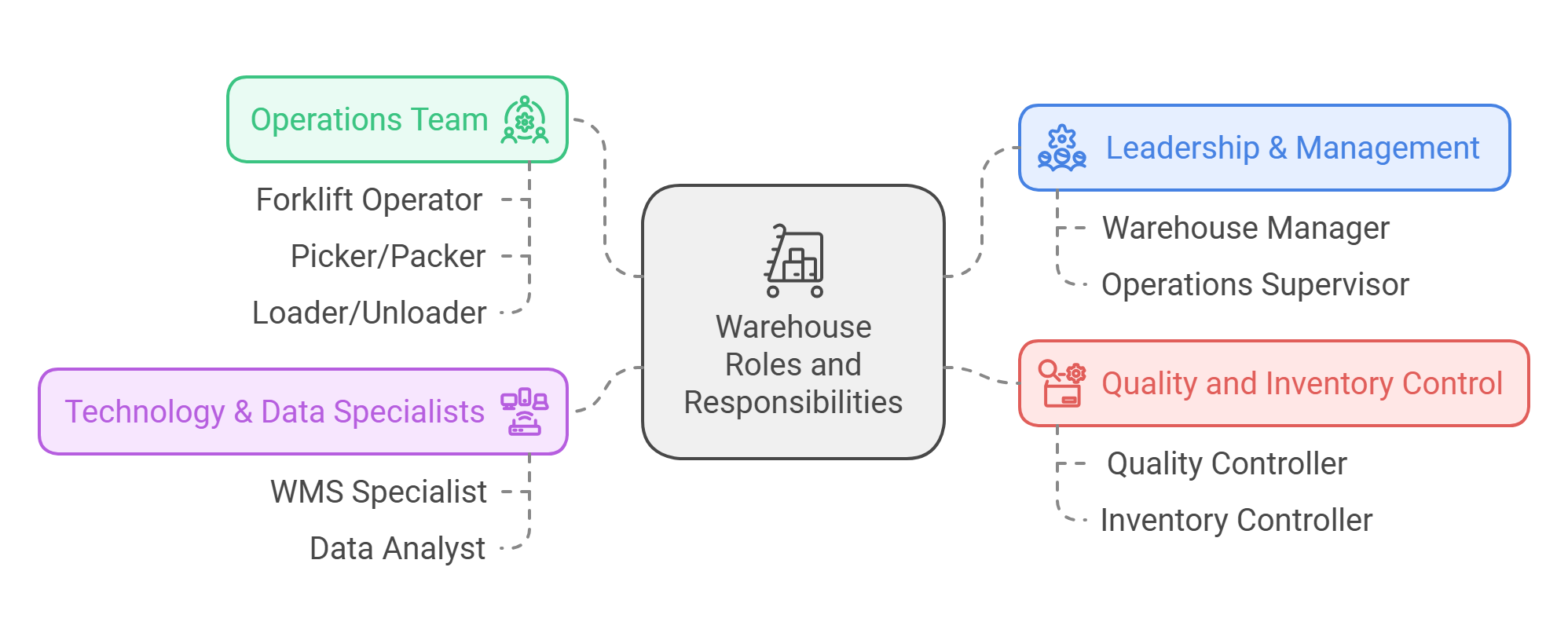
Key Roles and Their Responsibilities
1. Leadership & Management
Warehouse Manager:
- Develops operational strategies to meet business objectives.
- Monitors performance metrics like order accuracy and turnaround times.
- Ensures compliance with safety and regulatory standards.
Operations Supervisor:
- Oversees daily workflows, assigning tasks and resolving bottlenecks.
- Coordinates with different departments to ensure timely order processing.
- Addresses staffing issues and monitors team productivity.
2. Operations Team
Forklift Operator:
- Operates machinery to transport heavy goods and materials safely.
- Inspects forklifts for maintenance issues before use.
- Organizes goods for easy retrieval and efficient space utilization.
Picker/Packer:
- Reads order slips and retrieves items accurately.
- Packs goods securely for shipment, adhering to packing guidelines.
- Conducts quality checks to ensure item correctness before dispatch.
Loader/Unloader:
- Manages the loading and unloading of shipments manually or with equipment.
- Inspects goods for visible damage during the handling process.
- Ensures items are stored in designated locations promptly.
3. Quality and Inventory Control
Quality Controller:
- Conducts detailed inspections of inbound and outbound goods.
- Ensures packaging integrity and adherence to quality standards.
- Reports defects and coordinates with suppliers for resolutions.
Inventory Controller:
- Monitors stock levels using inventory management systems.
- Conducts regular cycle counts to maintain inventory accuracy.
- Resolves discrepancies and updates records accordingly.
4. Technology & Data Specialists
WMS Specialist:
- Implements and maintains the Warehouse Management System (WMS).
- Trains staff on WMS functionalities for smoother adoption.
- Troubleshoots system issues and ensures data integrity.
Data Analyst:
- Compiles operational data to identify trends and inefficiencies.
- Recommends actionable insights to optimize warehouse workflows.
- Tracks KPIs such as order accuracy and processing times.
Common Challenges in Warehouse Management
- Role Overlaps: Lack of clarity can result in inefficiencies and duplicated efforts.
- Technology Resistance: Employees may struggle to adapt to WMS or other digital tools.
- Labor Gaps: Difficulty in recruiting skilled workers impacts productivity.
- Inadequate Training: Poorly trained staff lead to errors and potential safety hazards.
A well-coordinated warehouse team is essential for efficient operations and high productivity. Understanding key roles and addressing challenges like training and labor shortages ensure seamless performance. Tools like WMS play a pivotal role in integrating and enhancing these processes.
Ready to streamline your warehouse operations? SellnShip’s WMS offers the solutions you need. Explore our WMS now!